What is Porosity in Welding: Recognizing Its Reasons and Enhancing Your Skills
What is Porosity in Welding: Recognizing Its Reasons and Enhancing Your Skills
Blog Article
Comprehending Porosity in Welding: Checking Out Causes, Results, and Avoidance Methods
Porosity in welding is a persistent obstacle that can dramatically influence the quality and stability of welds. As professionals in the welding industry are well mindful, understanding the causes, impacts, and prevention methods associated with porosity is important for accomplishing durable and reliable welds. By delving right into the origin of porosity, analyzing its damaging results on weld quality, and exploring effective avoidance techniques, welders can enhance their understanding and abilities to generate top notch welds constantly. The elaborate interplay of variables adding to porosity requires a comprehensive understanding and a proactive method to make certain successful welding results.
Typical Reasons For Porosity
Porosity in welding is mainly brought on by a mix of aspects such as contamination, inappropriate shielding, and poor gas coverage throughout the welding procedure. Contamination, in the form of dirt, grease, or corrosion on the welding surface area, develops gas pockets when warmed, causing porosity in the weld. Incorrect securing takes place when the protecting gas, frequently utilized in procedures like MIG and TIG welding, is not able to totally safeguard the molten weld swimming pool from responding with the surrounding air, leading to gas entrapment and succeeding porosity. Additionally, inadequate gas coverage, typically because of incorrect flow rates or nozzle positioning, can leave parts of the weld unsafe, permitting porosity to develop. These variables jointly contribute to the formation of gaps within the weld, weakening its honesty and potentially creating structural issues. Recognizing and attending to these usual reasons are vital actions in avoiding porosity and guaranteeing the quality and toughness of welded joints.
Effects on Weld Quality
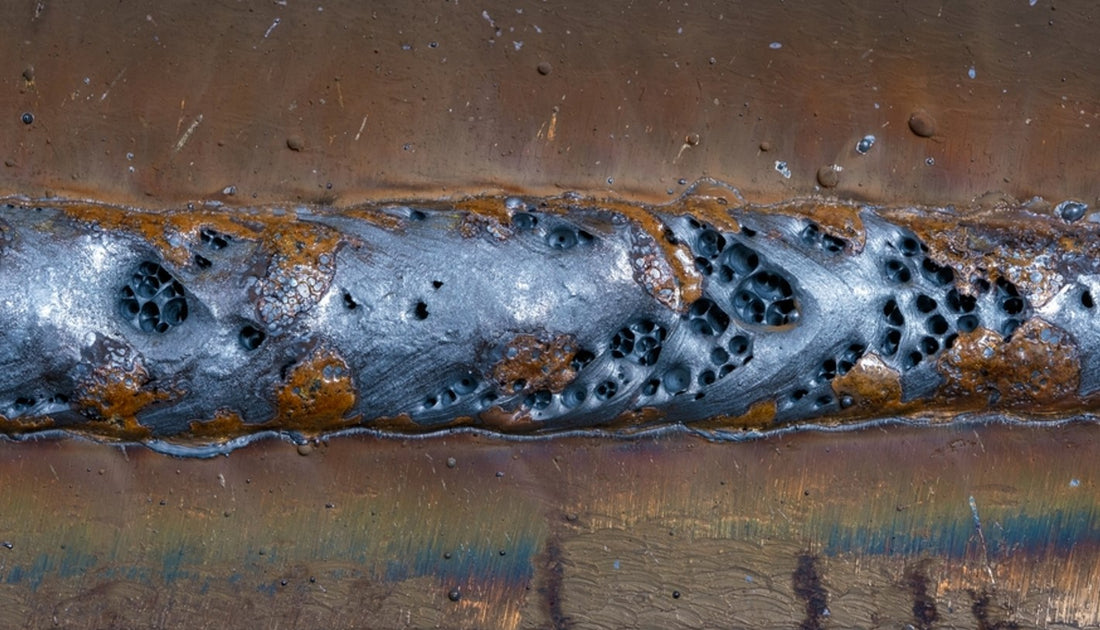
The presence of porosity in a weld can significantly compromise the general high quality and integrity of the bonded joint. Porosity within a weld creates voids or tooth cavities that damage the structure, making it more prone to cracking, deterioration, and mechanical failing. These spaces work as tension concentrators, minimizing the load-bearing ability of the weld and increasing the chance of early failure under applied anxiety. Furthermore, porosity can likewise serve as possible websites for hydrogen entrapment, further exacerbating the destruction of the weld's mechanical properties.
Moreover, porosity can hinder the efficiency of non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, making it testing to spot other defects or gaps within the weld. This can bring about substantial security problems, especially in crucial applications where the architectural stability of the bonded elements is extremely important.

Prevention Techniques Introduction
Offered the destructive effect of porosity on weld quality, efficient avoidance strategies are vital to preserving the architectural stability of welded joints. Additionally, choosing the ideal check it out welding parameters, such as voltage, current, and take a trip speed, can help lessen the risk of porosity formation. By incorporating these prevention methods into welding techniques, the occurrence of porosity can be significantly reduced, leading to more powerful and much more trustworthy welded joints.
Significance of Appropriate Shielding
Proper protecting in welding plays a critical function in preventing climatic contamination and making sure the integrity of bonded joints. Shielding gases, such as argon, helium, or a combination of both, are frequently made use of to secure the weld pool from responding with components in the air like oxygen and nitrogen. When these reactive components enter into call with the warm weld swimming pool, they can create porosity, resulting in weak welds with lowered mechanical homes.
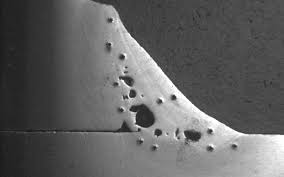
Inadequate protecting can result in numerous defects like porosity, spatter, and oxidation, compromising the architectural stability of the bonded joint. Sticking to proper securing methods is necessary to produce premium welds with marginal problems and make certain the long life and integrity of the welded elements.
Monitoring and Control Approaches
Just how can welders effectively keep an eye on and regulate the welding process to make certain optimal results and protect against issues like porosity? One trick technique is via using innovative monitoring innovations. These can consist of real-time monitoring systems that give comments on parameters such as voltage, present, travel speed, and gas flow rates. By continuously monitoring these variables, welders can recognize deviations from the optimal problems and make prompt modifications to avoid porosity formation.

Additionally, implementing correct training programs for welders is vital for checking and controlling the welding process efficiently. What is Porosity. Educating welders on more information the significance of keeping consistent criteria, such as proper gas securing and travel rate, can help avoid porosity problems. Normal assessments and accreditations can also make sure that welders excel in surveillance and regulating welding procedures
Moreover, the usage of automated welding systems can improve surveillance and control capabilities. These systems can precisely control welding criteria, reducing the probability of human error and guaranteeing consistent weld high quality. By combining sophisticated monitoring technologies, training programs, and automated systems, welders can effectively check and manage the welding process to lessen porosity flaws and accomplish high-grade welds.
Conclusion

Report this page